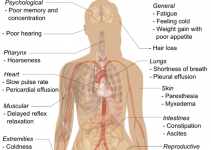
Helicobacter pylori are kind of bacteria, usually found in the stomach, and are one of the most common causes of stomach cancer. About two-thirds of the world’s populations have this germ. Researchers aren’t even sure how it gets into the body, but it is believed to spread through unclean food and water.
But other than stomach pathologies, we’ll discuss the bacteria’s possible effect on fertility, pregnancy, and on the unborn child in this article.
Before addressing how it can affect those areas mentioned above, it’s best to take a closer look at a Helicobacter pylori infection.
Symptoms of Helicobacter pylori infection
The odd thing about a Helicobacter pylori infection is that you don’t experience any symptoms when infected. Instead, the infection comes into notice when you develop signs of a peptic ulcer disease (PUD).
Once the bacteria get into the body, it can live there for many years. Over time, it can cause sores (ulcers) in the stomach lining.
However, most of those who have the bacteria don’t even have ulcers or experience any symptoms. But the good news is that those who get infected can take medicines to get rid of the germs.
How Helicobacter pylori infects people
In the past, ulcers were thought to be caused by eating spicy foods, stress, smoking, or any other bad lifestyle habits. The discovery of Helicobacter pylori in 1982 showed that it could be traced as the culprit for most stomach ulcers.
Helicobacter pylori attack your stomach’s lining once it gets inside your body. That lining is supposed to serve as protection from the acid secreted by your body to digest food.
A significant damage caused by the bacteria allows acid to get through the protective lining, which leads to ulcers that can bleed or prevent food from moving through the digestive tract.
It is believed that food, water, or utensils can be sources for the bacteria. It is also common in places with no access to clean water or good sewage systems.[1]
The bacteria can also be picked up through contact with the saliva or any other body fluid of infected people.
A lot of people get infected during childhood, but it can happen to adults too.
Helicobacter pylori infection effect on fertility
An article published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology in 2014 called Can Helicobacter pylori infection influence human reproduction? It’s concluded that there is a “decrease in reproductive potential” in individuals affected by the germ.
The study also found that the infection is even more common in people with fertility disorders. Women who are infected with H. pylori have anti-Helicobacter pylori antibodies in cervical mucus and follicular fluid which decrease sperm motility.
Men who are infected also have decreased sperm motility and viability.
A January 2014 article in the World Journal of Gastroenterology, Helicobacter pylori, and pregnancy-related disorders, found that an infection is linked with hyperemesis gravidarum, a severe form of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
The study states that a Helicobacter pylori infection can play a part in the development of several pregnancy-related disorders through various mechanisms.
For one, it can be involved in the depletion of micronutrients, resulting in maternal anemia and fetal neural tube effects. It can also play a role in preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction, and miscarriage.
A Helicobacter pylori infection is almost always acquired before pregnancy. It is believed that the changes, both hormonal and immunological, that happen during pregnancy activate latent Helicobacter pylori.
The activation of the bacteria produces negative effects not only on the mother, but also on the unborn child, with insufficient growth, malformation, and death as possible effects.
Helicobacter pylori infection effect on the fetus.
The study, Helicobacter pylori and pregnancy-related disorders, published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology in January 2014 found that Helicobacter pylori are linked with many pregnancy-related diseases.
Also, the diseases are potentially life-threatening not only for the mother but also for the child.
Who is at risk of contracting Helicobacter pylori infection?
As mentioned, the bacteria are often contracted during childhood. However, adults can also be affected.
The following conditions make you more susceptible to contracting infection:
- Living in a crowded environment. The chances of getting infections increase if the home you live in has a bathroom that is shared by many others.
- Living in a place without good a clean water supply. Access to clean water is extremely important to avoiding infection, not just of Helicobacter pylori but any kind.
- Living in a developing country. A number people in developing countries don’t live in sanitary conditions. Plus, they mostly live in crowded environments. The combination of both increases the risk of getting an infection.
- Living with someone infected with Helicobacter pylori. The bacteria can be contracted through saliva or any other bodily fluid[2]. Food, water, and utensils can also be sources for the bacteria.
How can Helicobacteria pylori be prevented?
Here are a few good practices to employ:
- Always wash your hands. This is especially important after you’ve used the bathroom. It’s also equally important to do so before you prepare or eat food. If you have children, make sure they know the importance of doing so.
- Do not consume dirty food or water. This is rather hard to avoid because you don’t know how the food was prepared. You can either trust brands that have done well with food safety or make your food.
- Make sure everything you eat is cooked thoroughly. This isn’t just to avoid Helicobacter pylori – it also applies to all sorts of infections you can get from eating undercooked food.If at a restaurant, there’s nothing wrong with sending back food requesting that it be cooked thoroughly.
- Do not accept food from people who haven’t washed their hands. This is very difficult to adhere because you just don’t know how others prepare their food. But it’s easier to do this in bakeries and similar shops where you can see how they handle food served to you.
The best way to avoid Helicobacter pylori is through cleanliness. Observe sanitary practices all the time, not just when you are trying to get pregnant or are already carrying a child.
References